Alignment of two whole genome sequences can be very useful in comparative genomics and it is particularly helpful when alignments are visualized. By this type of analysis, you will be able to find:
- Gene synteny
- Genomic structural difference caused by duplication, inversion, deletion and insertion.
- Identification of extra-chromosomal elements (e.g. a plasmid in one genome is integrated in the second genome).
MUMMER is a suite of bioinformatics programs developed by Kurtz et al. (2004) and it’s available here. NUCMER is a program that is part of the suite designed for pairwise whole genome alignment and more information about NUCMER can be found here. Here, we will explain how to interpret results of the analysis.
A pair of well aligned genomes
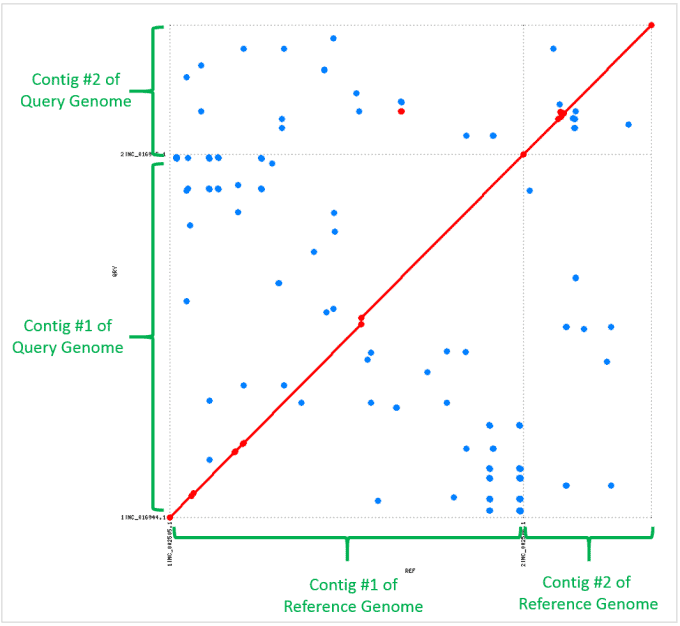
Whole genome alignment reveals two inversions
- Alignments with blue color indicates inversions in both contigs #1 and #2.
Query genome has a large, extra unique contig\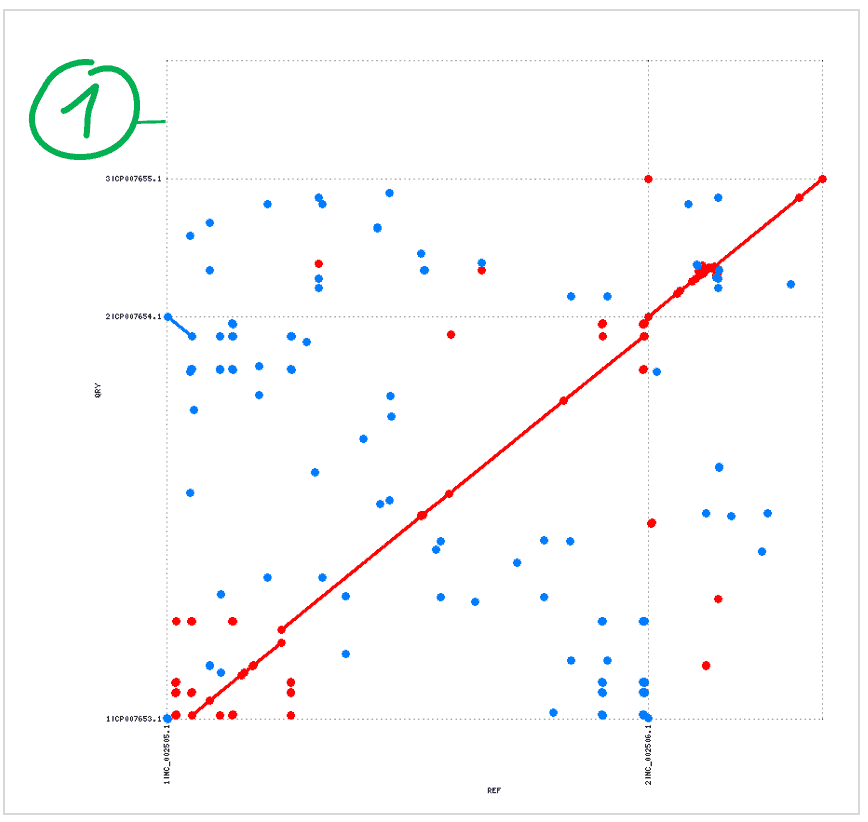
- There is no homology between contig #3 of query genome and the contigs of reference genome.
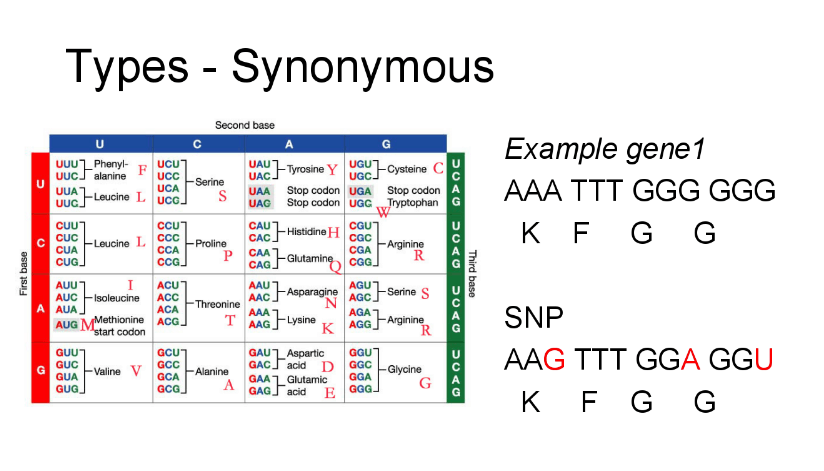
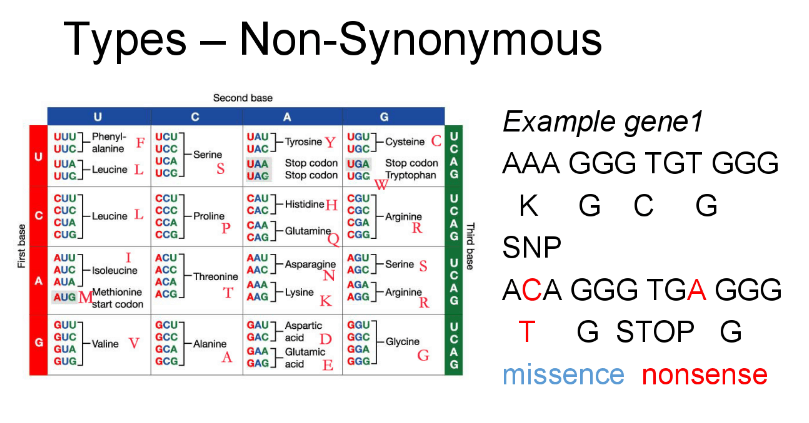
Single Nucleotide Polymorphism(SNP) analysis
In addition to the genome alignment plot, our new update includes SNP analysis that provides user friendly SNP table. With the aid of SNP analysis, you can easily distinguish the types of SNPs (insertion, deletion, and substitution) and mutations (intergenic, synonymous, or non-synonymous) if SNP bases are under 8000.
Each SNP bases were found with NUCMER (a genome alignment program) and the types of mutations are obtained with CJ Bioscience’s unique pipeline. The description of mutation types is given below.
Updated on Oct 14th, 2016 (SH)